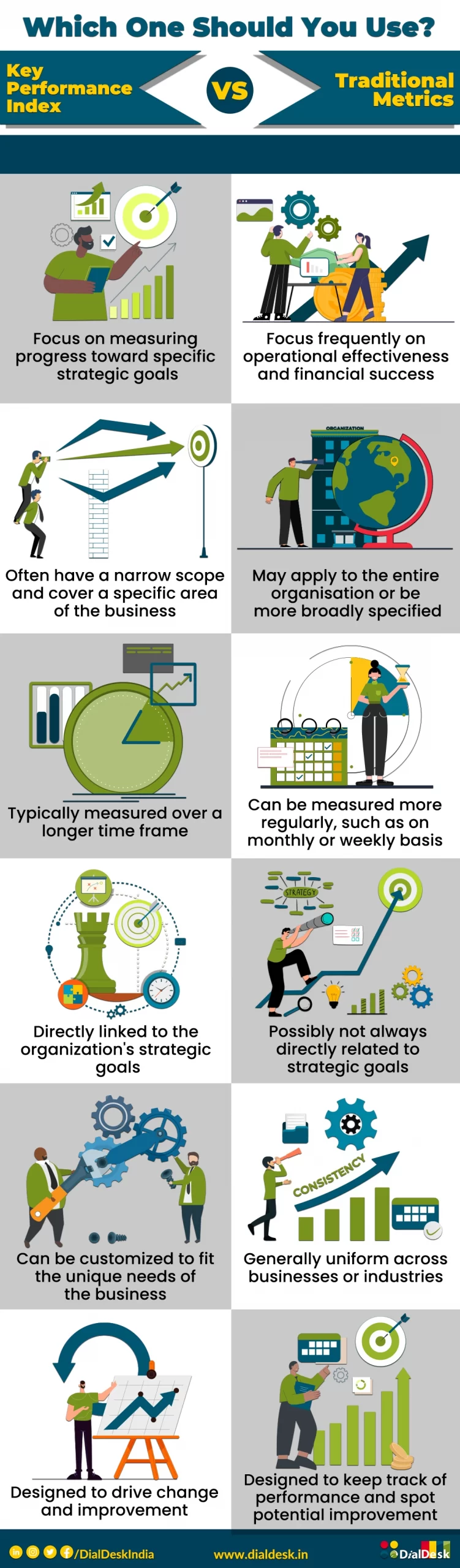
How do KPIs Work and What Exactly are They?
In basic English, a KPI is a quantifiable value that shows how effectively a company is achieving its objectives. KPIs can be used to evaluate performance at several levels within an organisation, including that of specific employees, entire departments, and the overall operation. Since they are typically exact, quantitative, and time-bound, it is easy to gauge progress and spot areas that need improvement.
Depending on their objectives and industry, organisations might utilise a wide range of KPIs. For instance, a sales team may assess its success using KPIs like sales growth, customer acquisition rate, and conversion rate. In contrast, a manufacturing company may track its success using KPIs like production efficiency, quality defect rate, and on-time delivery.
KPIs are wonderful because they can be tailored to meet the demands of each organisation. Setting and monitoring KPIs can help you stay focused on what matters most and make data-driven decisions that can advance your business, regardless of how big or small your company is.
Major Benefits of KPIs
Here are the major benefits of KPIs:
-
Improved Performance Tracking
The ability for firms to track their performance over time is one of KPIs’ primary advantages. Businesses can acquire insightful information about their performance and pinpoint areas for growth by creating precise goals and tracking progress towards them. For instance, a marketing team may decide to make it their KPI to boost website traffic by 20% over the following six months. They can improve their performance and finally hit their aim by monitoring their progress towards this goal and making necessary adjustments to their strategies and tactics.
-
Enhanced Decision-Making
KPIs can aid firms in decision-making by giving them a clear picture of their performance. Companies may decide wisely on resource allocation, product development, and strategic planning by having access to accurate and current data. For instance, a manufacturing organisation may use KPIs like production efficiency and defect rate to pinpoint areas where its production processes need to be improved. They may make wise decisions about how to deploy resources and boost their overall performance by studying this data.
-
Increased Accountability
By establishing clear expectations and objectives for workers and teams, KPIs can support accountability within a firm. Companies can hold employees accountable for their work and make sure that everyone is pursuing the same aims by monitoring performance against these goals. This can enhance overall productivity and foster an outstanding culture inside the company.
-
Improved Communication
By giving employees at a company a consistent vocabulary and framework for discussing performance, KPIs can also enhance internal communication. Teams can communicate more effectively and cooperate towards a common objective by establishing a clear set of KPIs that everyone can comprehend. Through the dismantling of silos, a more integrated and collaborative work environment may be created.
-
Competitive Advantage
The ability to make data-driven decisions and maintain focus on their objectives is another way that KPIs may give firms a competitive edge. Companies may set themselves apart from the competition and provide greater value to their customers by monitoring their performance and making constant changes. This could be a vital asset that distinguishes firms in today’s fiercely competitive business environment and aids in their success.
Conclusion
Setting and monitoring KPIs is crucial for any firm that wants to stay on track and accomplish its objectives in the fast-paced and fiercely competitive business world of today. KPIs give companies a framework for assessing performance, making knowledgeable choices, raising accountability, enhancing communication, and obtaining a competitive edge. Businesses can obtain important insights into their performance and continuously enhance their procedures to stay ahead of the competition by defining clear, quantifiable, and time-bound goals.